Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
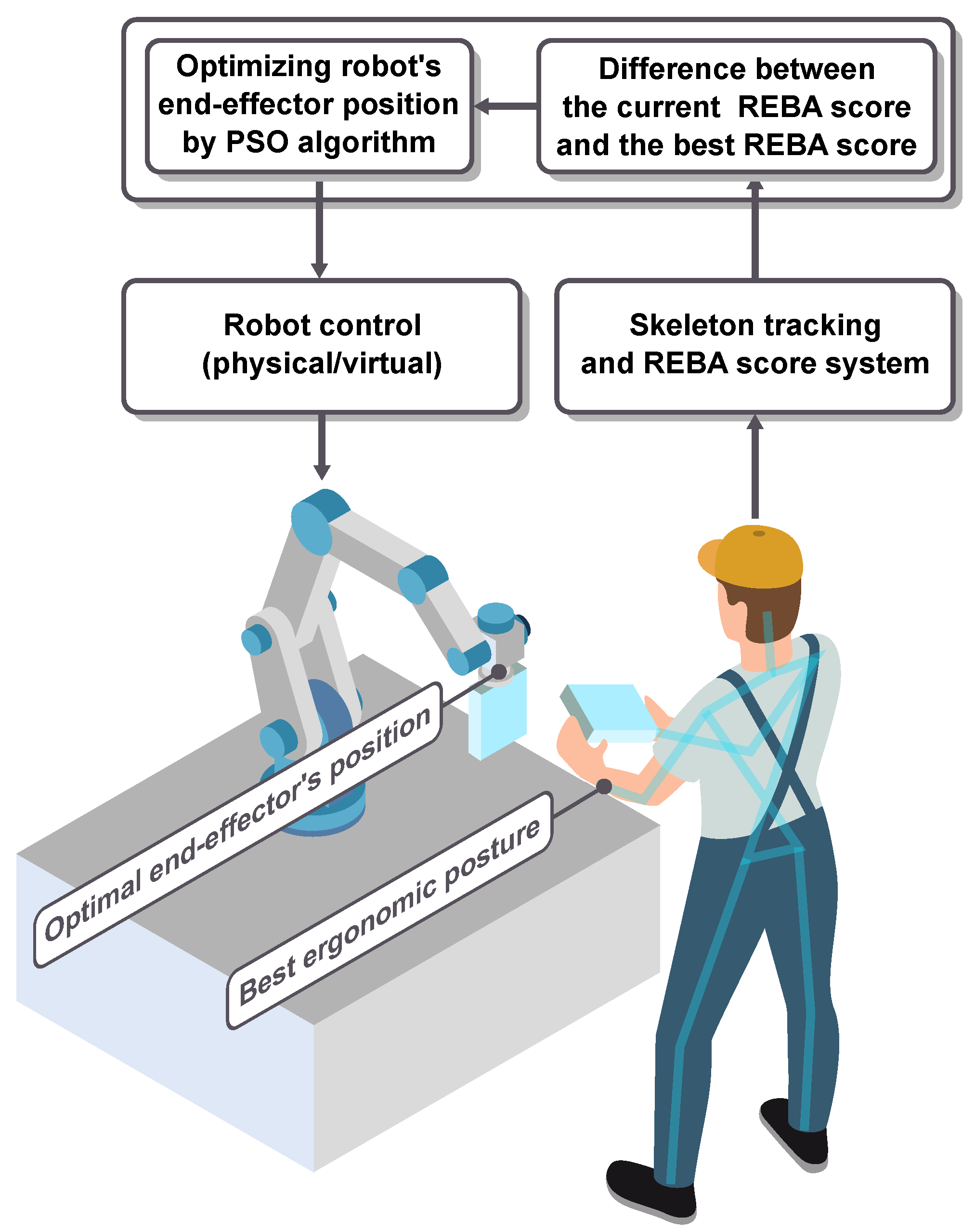
Musculoskeletal disorders caused by poor work posture are a serious concern in the industry since they lead to absenteeism and medical leave from work. In the context of human–robot collaboration, this issue can be mitigated if collaborative robots support human workers to perform their tasks more ergonomically. In this work, we propose a method to optimize human posture during human–robot collaboration using the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm. Our approach involves assigning an appropriate location to the robot’s end-effector to minimize the distance between the optimized posture of the human and their current posture in the working space. To measure human posture, we use the Rapid Entire Body Assessment score (REBA) calculated from body joint angles captured by a Kinect camera. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, we conducted a user study with 20 participants in a virtual reality environment. The PSO algorithm could position the robot end-effector to the optimal position close to real time. Our results showed that our method could improve ergonomics by 66%, indicating its potential for use in human–robot collaborative applications.
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, Synthetic Dye
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, kurnik copas

CORE & PubMed collaborate for further full text dissemination – CORE
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, twitter codes project ghoul
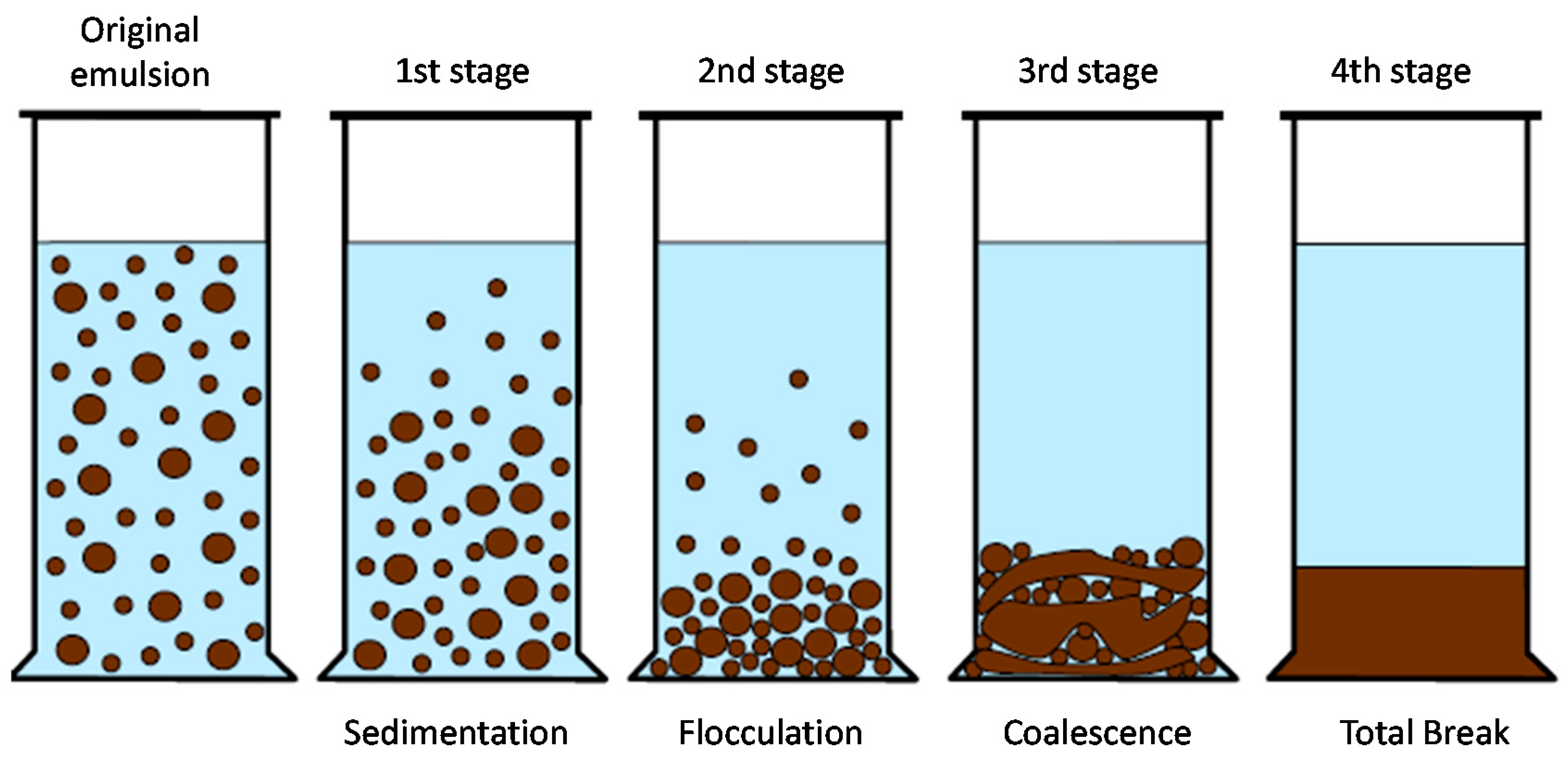
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, Emulsion
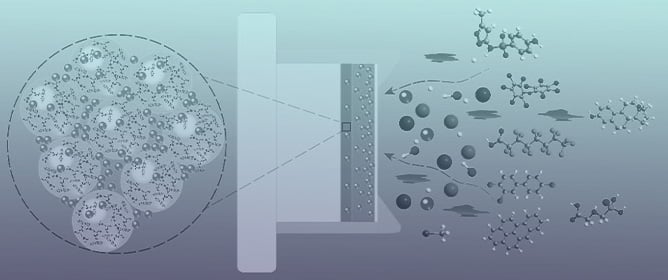
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, rainy days v cifra

Applied Science and Technology Full Text

Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, groups moodle ufsc
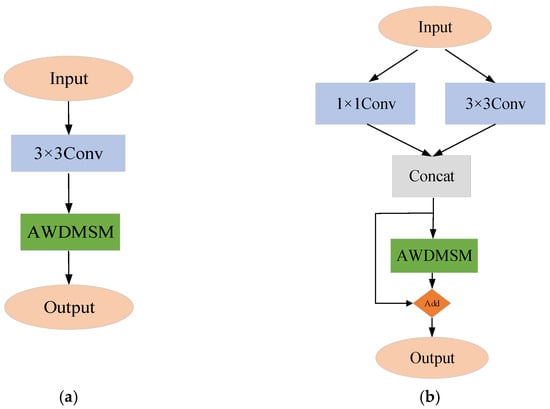
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, g1 f1800

Introduction to libre « fulltext » technology

Science Pickens County Library System







