The role and therapeutic potential of stem cells in skeletal
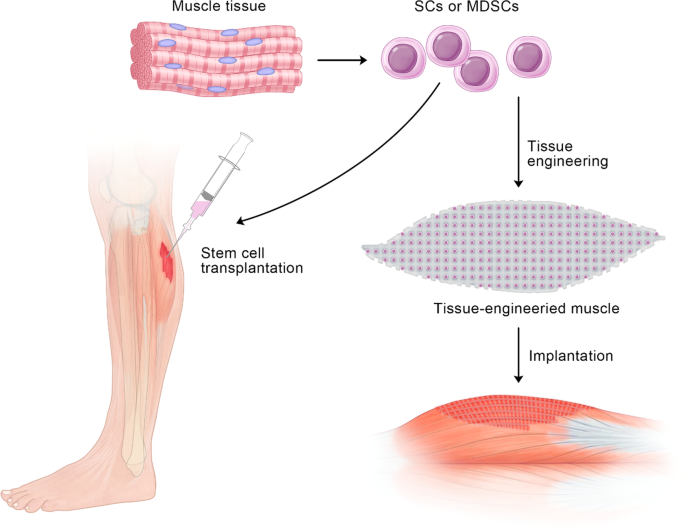
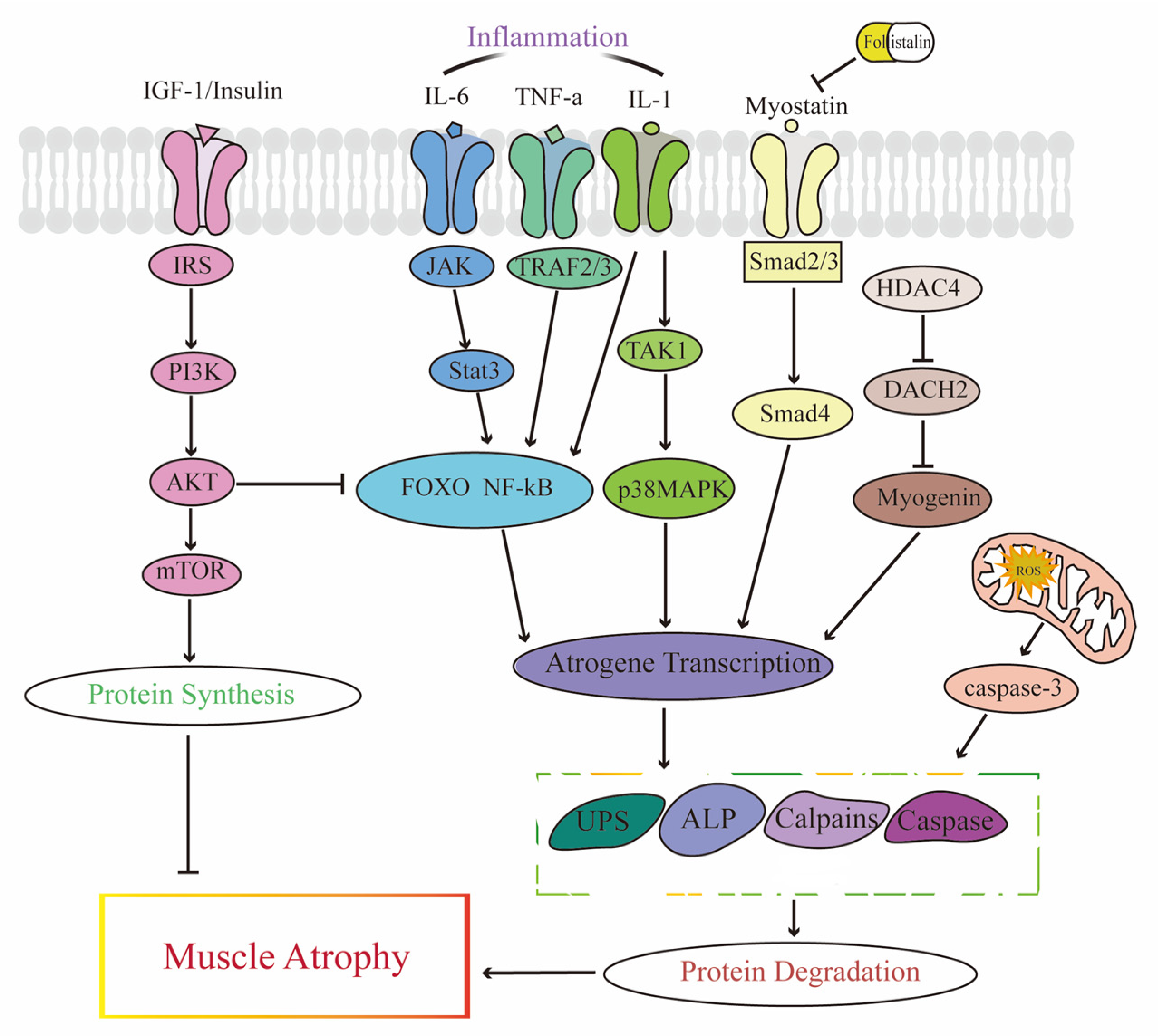
Sarcopenia is a common age-related skeletal muscle disorder featuring the loss of muscle mass and function. In regard to tissue repair in the human body, scientists always consider the use of stem cells. In skeletal muscle, satellite cells (SCs) are adult stem cells that maintain tissue homeostasis and repair damaged regions after injury to preserve skeletal muscle integrity. Muscle-derived stem cells (MDSCs) and SCs are the two most commonly studied stem cell populations from skeletal muscle. To date, considerable progress has been achieved in understanding the complex associations between stem cells in muscle and the occurrence and treatment of sarcopenia. In this review, we first give brief introductions to sarcopenia, SCs and MDSCs. Then, we attempt to untangle the differences and connections between these two types of stem cells and further elaborate on the interactions between sarcopenia and stem cells. Finally, our perspectives on the possible application of stem cells for the treatment of sarcopenia in future are presented. Several studies emerging in recent years have shown that changes in the number and function of stem cells can trigger sarcopenia, which in turn leads to adverse influences on stem cells because of the altered internal environment in muscle. A better understanding of the role of stem cells in muscle, especially SCs and MDSCs, in sarcopenia will facilitate the realization of novel therapy approaches based on stem cells to combat sarcopenia.

Therapeutic potential of stem cells against different diseases
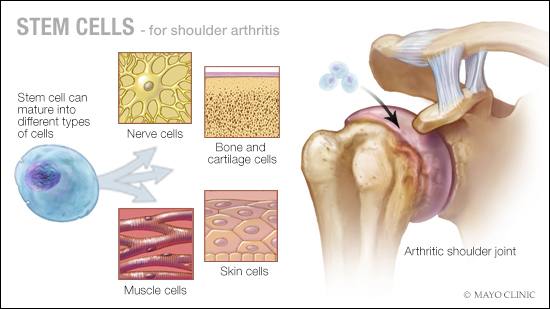
Mayo Clinic Q and A: Stem cell therapy for arthritis - Mayo Clinic
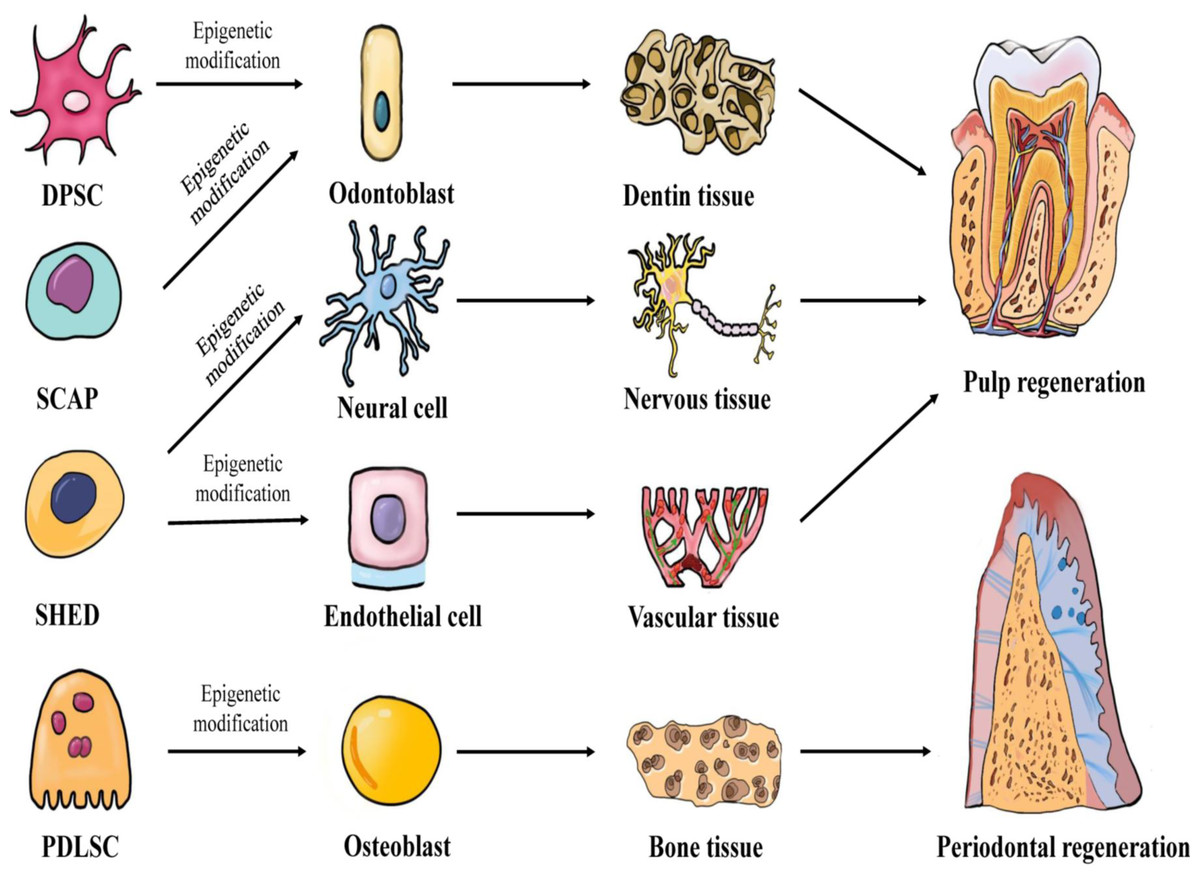
Epigenetic regulation of dental-derived stem cells and their
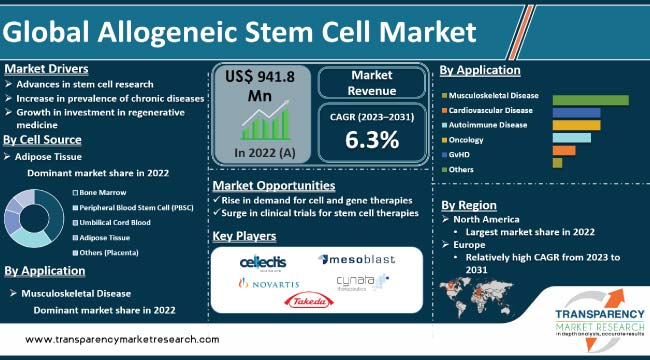
Allogeneic Stem Cell Market Size, Share & Statistics, 2031

A recent report from NYU - NYU Grossman School of Medicine
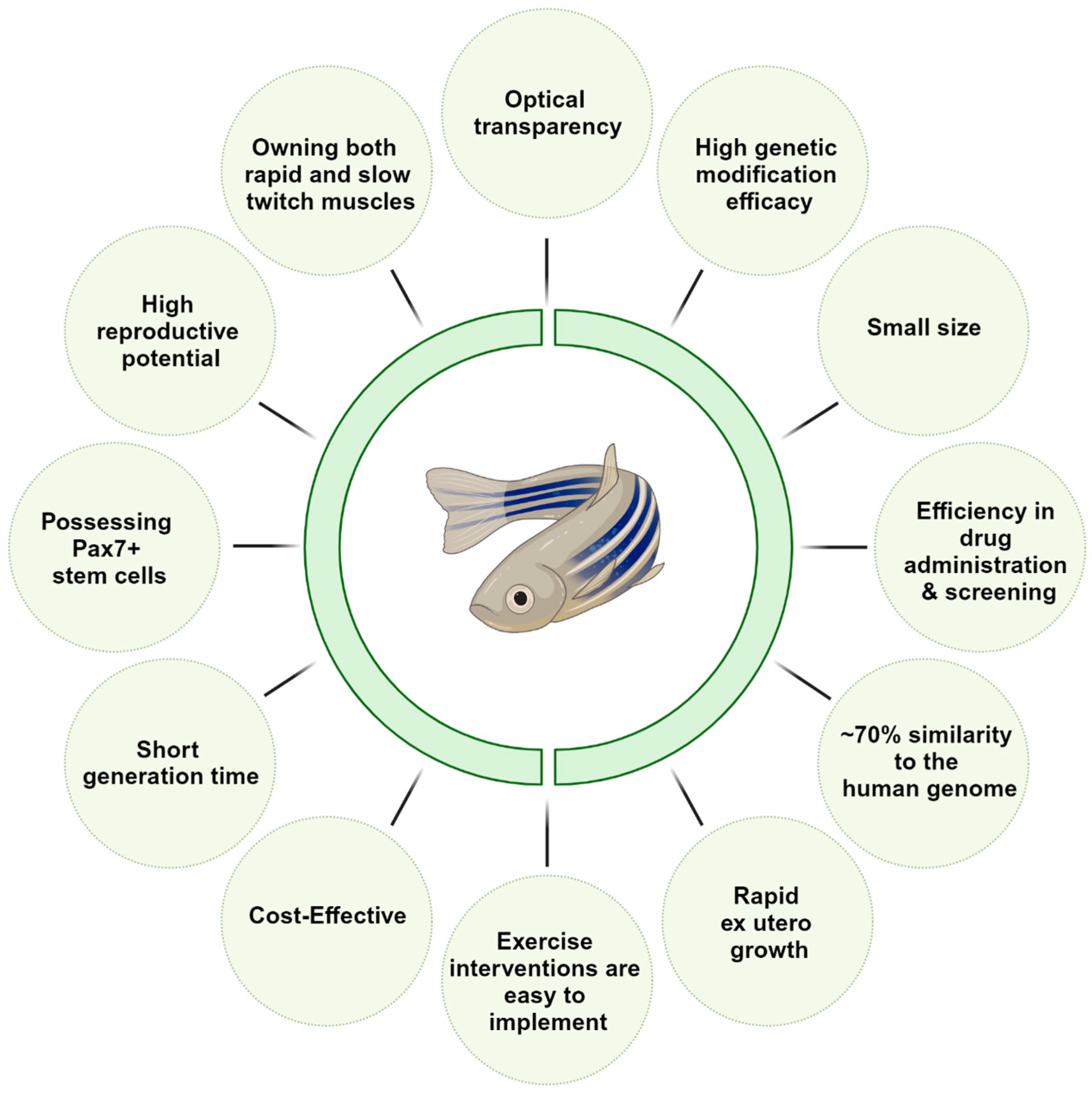
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Pooled evidence from preclinical and clinical studies for stem

Adult stem cell sources for skeletal and smooth muscle tissue

Clonal Differentiation of Skeletal Muscle–Derived CD34−/45− Stem Cells Into Cardiomyocytes In Vivo

Embryonic Cord Transplants in Peripheral Nerve Restore Skeletal Muscle Function
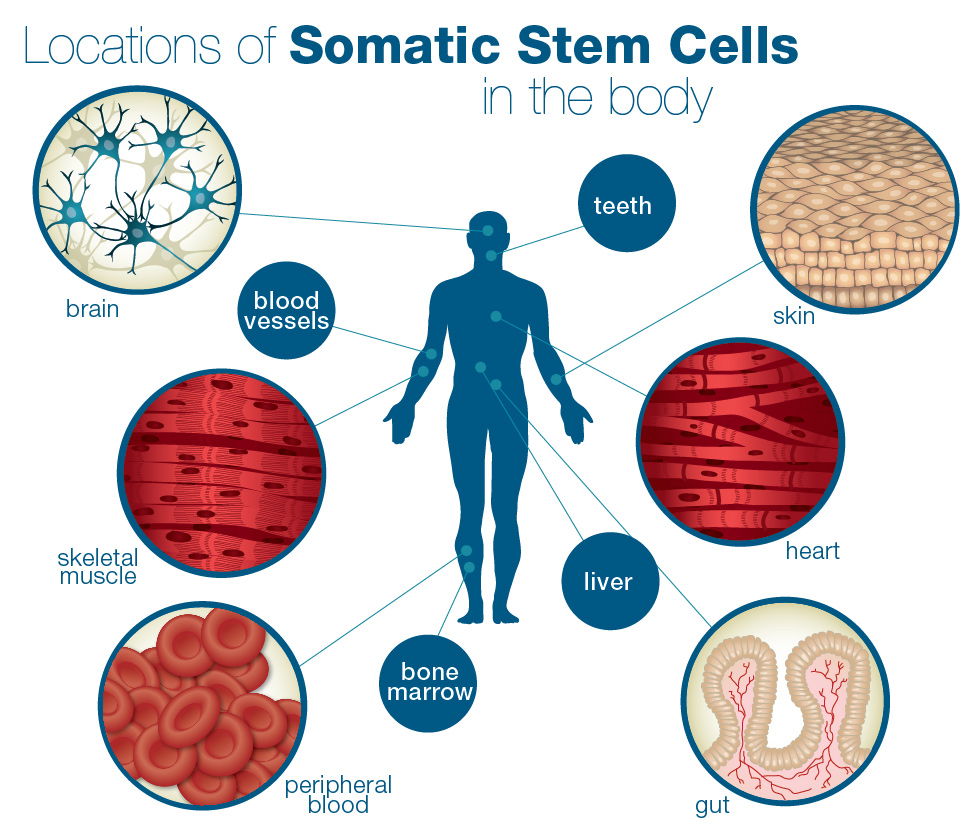
Stem Cell Quick Reference

Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells/dental stem
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text