Evaluating coverage bias in next-generation sequencing of Escherichia coli
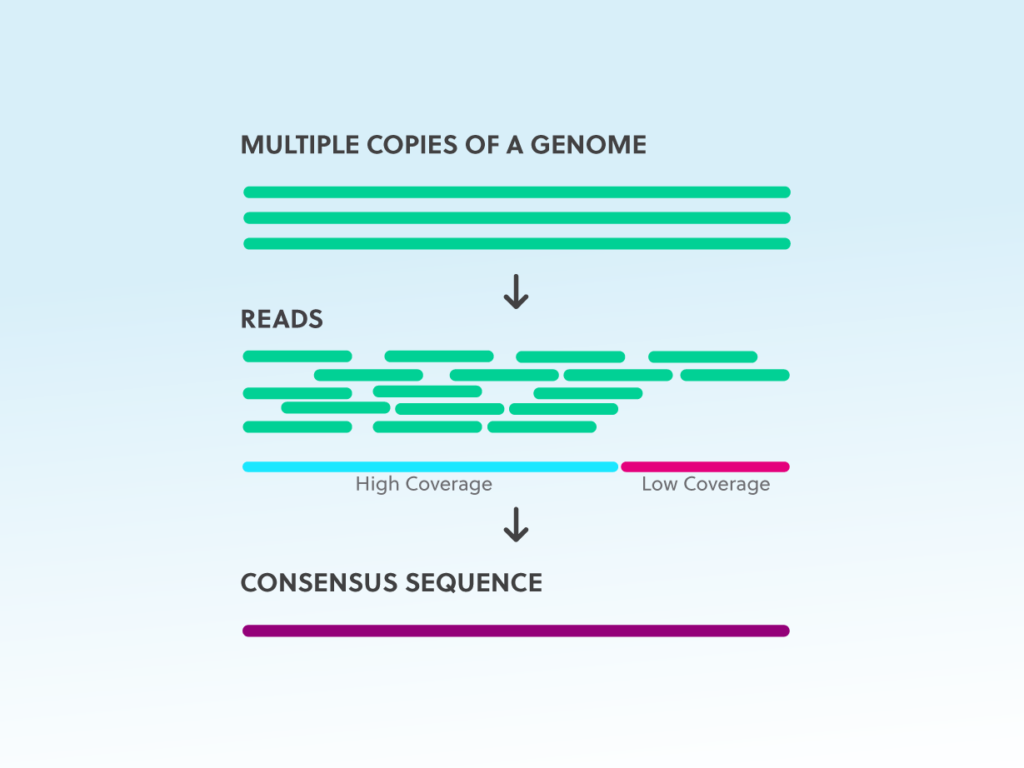
Whole-genome sequencing is essential to many facets of infectious disease research. However, technical limitations such as bias in coverage and tagmentation, and difficulties characterising genomic regions with extreme GC content have created significant obstacles in its use. Illumina has claimed that the recently released DNA Prep library preparation kit, formerly known as Nextera Flex, overcomes some of these limitations. This study aimed to assess bias in coverage, tagmentation, GC content, average fragment size distribution, and de novo assembly quality using both the Nextera XT and DNA Prep kits from Illumina. When performing whole-genome sequencing on Escherichia coli and where coverage bias is the main concern, the DNA Prep kit may provide higher quality results; though de novo assembly quality, tagmentation bias and GC content related bias are unlikely to improve. Based on these results, laboratories with existing workflows based on Nextera XT would see minor benefits in transitioning to the DNA Prep kit if they were primarily studying organisms with neutral GC content.
Cells, Free Full-Text
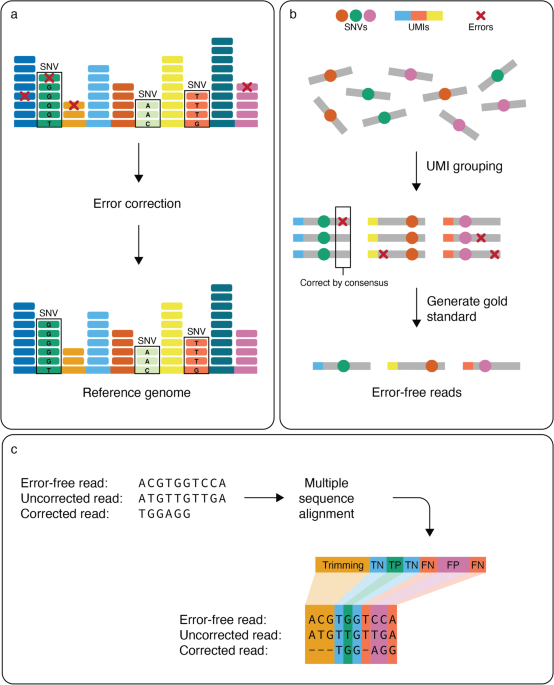
Benchmarking of computational error-correction methods for next-generation sequencing data, Genome Biology

PDF] Summarizing and correcting the GC content bias in high-throughput sequencing
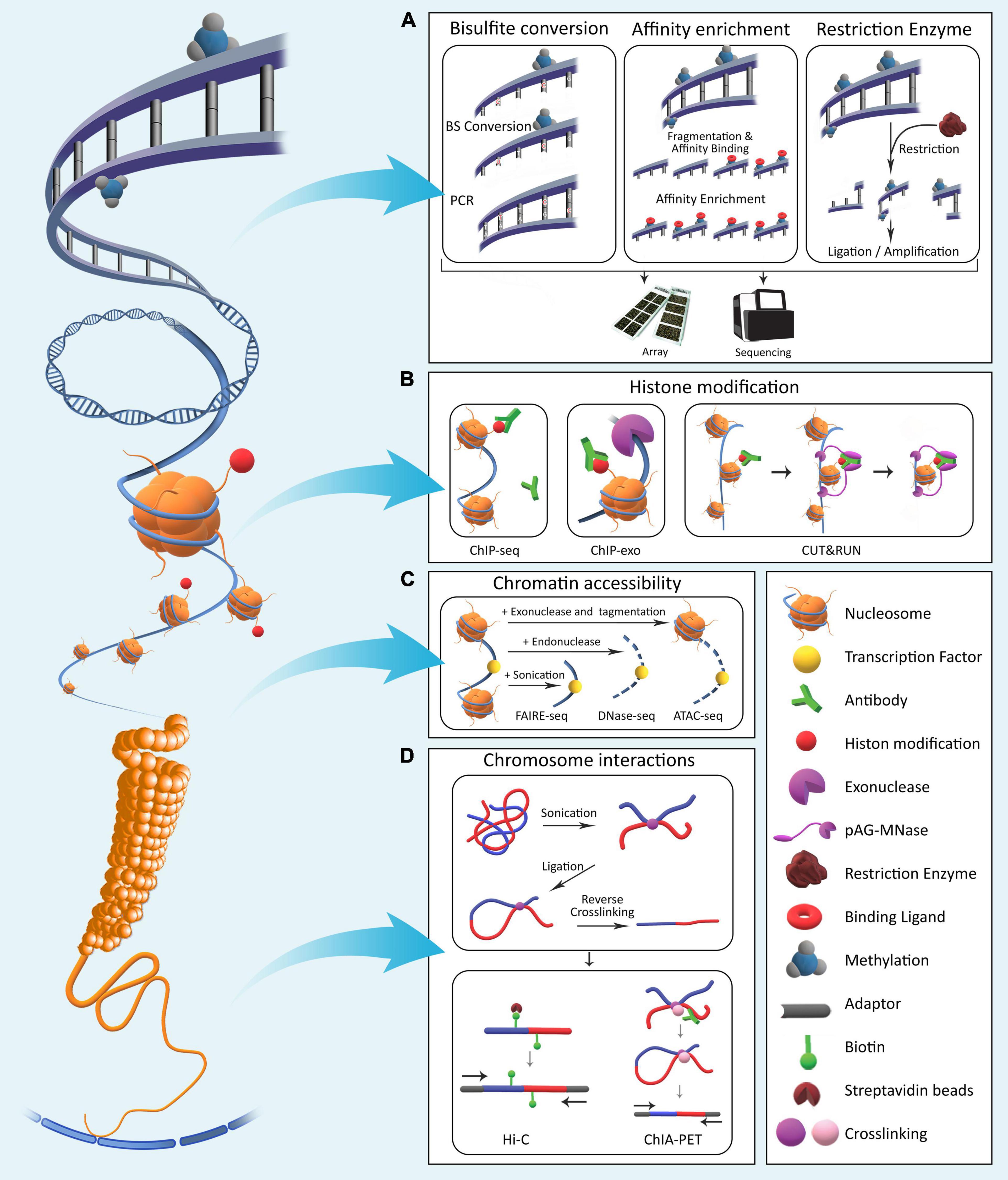
Frontiers A Comparative Overview of Epigenomic Profiling Methods
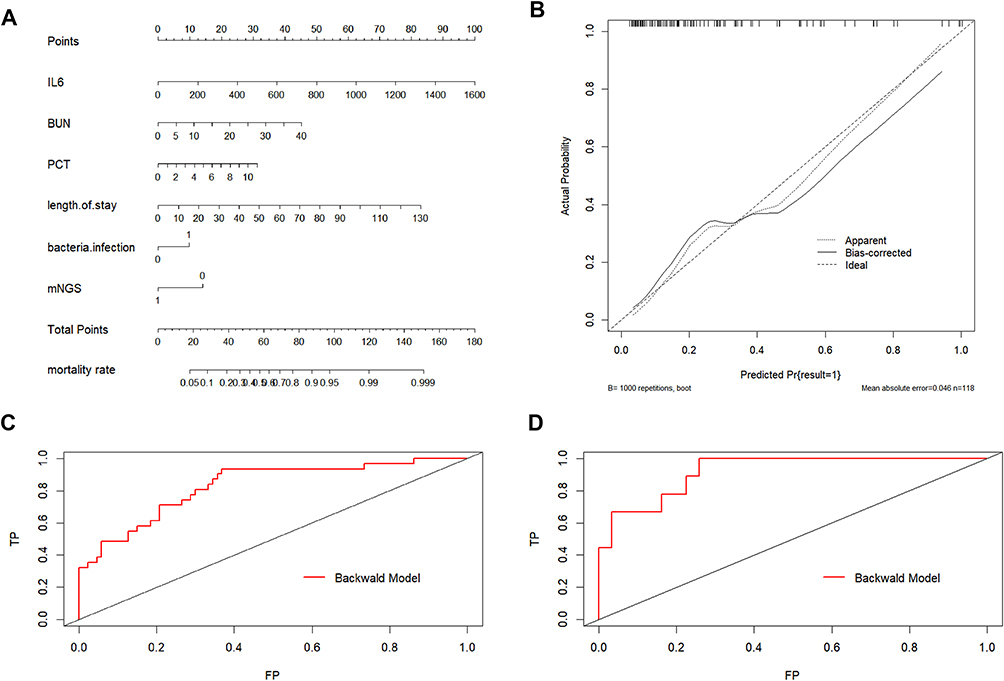
Clinical Evaluation of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing and Iden

A) Pangenome analysis of the assembled whole genome sequence of two MTB
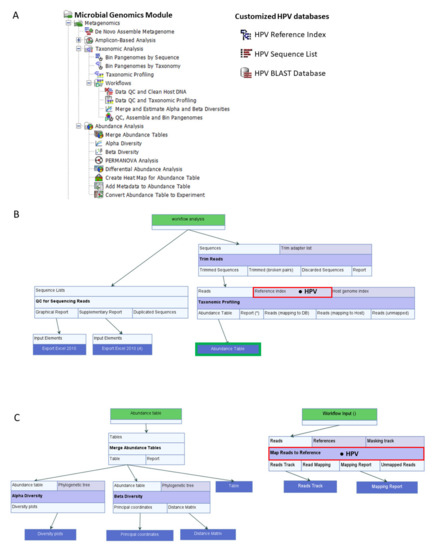
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

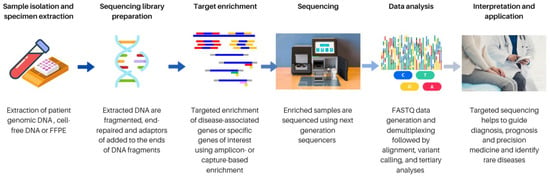
Library preparation for next generation sequencing: A review of automation strategies - ScienceDirect

Evaluating the performance of (A) lg(RPKM), (B) genomic coverage, and
Evaluating coverage bias in next-generation sequencing of Escherichia coli - Murdoch University